In today’s fast‑changing world, organizations and individuals must be prepared for uncertainty. Whether it’s cyber threats, economic shifts, natural disasters, or personal challenges, resilience determines who survives and who thrives. But have you ever asked, what are the 5 key stages of resilience lifecycle framework that help people and systems endure adversity and grow stronger? In this article, we break down each stage with simple explanations, practical insights, and real‑world examples to help you apply this powerful framework yourself.
The resilience lifecycle framework is more than a concept it’s a strategic approach to anticipating, preparing, responding, recovering, and adapting to disruptions. Understanding these stages can significantly strengthen your ability to withstand and learn from change.
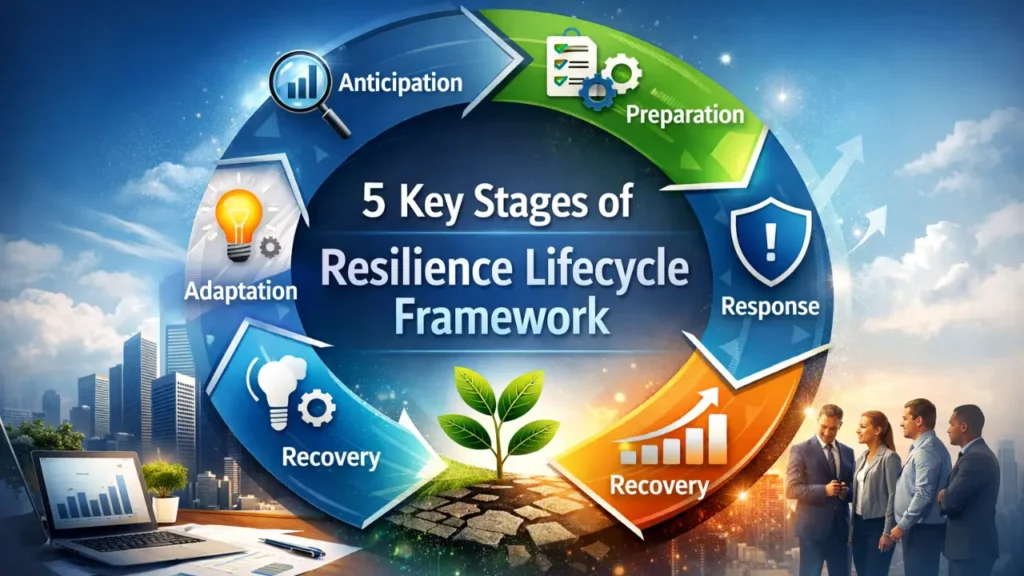
What Are the 5 Key Stages of Resilience Lifecycle Framework?
The resilience lifecycle framework provides a structured, cyclical approach for strengthening resilience over time. Unlike reactive models that address problems after they occur, this framework helps anticipate disruptions and evolve stronger systems and behaviors. The five stages are Anticipation, Preparation, Response, Recovery, and Adaptation.
Stage 1 Anticipation (Recognizing Risks Before They Hit)
Anticipation is the foundation of resilience. This stage focuses on identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities before they become crises. It’s about foresight recognizing trends, patterns, and early warning signs that could affect operations or well‑being.
Activities in the Anticipation Stage:
- Conduct regular risk assessments
- Use predictive analytics and scenario planning
- Monitor external trends and internal signals
- Encourage proactive thinking across teams
Real‑world example: A tech company conducts continuous cybersecurity scans and threat prediction reports to spot vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them.
Key Benefit: Anticipation reduces surprises and creates space for thoughtful planning and decision‑making.
Stage 2 Preparation (Planning and Strengthening)
Once risks are identified, preparation turns insight into readiness. This is where planning, training, and resource allocation occur. Preparing doesn’t mean hoping for the best it means building a capability to act confidently under pressure.
Preparation Actions:
- Develop clear contingency plans
- Train teams via simulations and drills
- Allocate necessary tools, finances, and personnel
- Establish communication protocols
Real‑world example: A hospital runs emergency drills to prepare staff for mass casualty events, ensuring they can respond smoothly under stress.
Outcome: Better preparation decreases panic and improves decision quality when disruptions occur.
Stage 3 Response (Taking Swift, Effective Action)
When a disruption hits, the response stage begins. This stage activates the plans and systems built earlier, focusing on minimizing damage and maintaining stability. A successful response is deliberate led by trained people and supported by clear communication.
Elements of an Effective Response:
- Activate crisis management teams
- Communicate clearly with stakeholders
- Implement predefined action steps
- Adjust as needed based on real‑time information
Real‑world example: During a cyberattack, the IT and security teams follow their incident response playbook, isolating affected systems and notifying customers within minutes.
Result: A strong response can significantly reduce downtime, financial loss, and reputational harm.
Stage 4 Recovery (Restoring and Rebuilding)
The recovery stage moves beyond immediate crisis handling. Here, the focus is on restoring normal operations and emerging stronger. Recovery isn’t just repair; it’s reflection and improvement.
Recovery Actions:
- Repair damaged systems or processes
- Evaluate what failed and why
- Support people’s emotional well‑being
- Use backups and continuity plans effectively
Real‑world example: After a hurricane, a community not only rebuilds infrastructure but also upgrades flood defenses to prevent future damage.
Benefit: The recovery stage closes the gap between chaos and growth.
Stage 5 Adaptation (Evolving Through Lessons Learned)
Adaptation is the most transformative stage. Lessons from disruptions are integrated into strategies, systems, and culture. This is where continuous improvement happens responding to change not just with fixes, but with evolution.
Adaptation Strategies:
- Conduct post‑incident reviews
- Update policies and procedures
- Train teams based on new insights
- Innovate systems to reduce future risks
Real‑world example: After supply chain issues, a company diversifies its suppliers and automates order forecasting to prevent future disruptions.
Impact: Adaptation turns resilience into a competitive advantage and prepares you for the next cycle.
Why Understanding the Framework Matters
Understanding what are the 5 key stages of resilience lifecycle framework is crucial because it helps you intentionally build long‑term strength rather than merely reacting to crises. Here’s how embracing this framework benefits you:
- Improves preparedness before crises strike
- Enhances response speed and quality
- Supports quicker recovery and less downtime
- Encourages learning and continuous improvement
- Builds confidence among stakeholders
This makes resilience a strategic capability, not a reactive tactic.
Practical Tips for Implementing the Framework
Whether you’re leading a team or improving your personal resilience, apply these actionable steps:
Start Small:
Test the framework on a single project or department before scaling.
Measure What Matters:
Track key metrics (e.g., recovery time, response accuracy, staff readiness).
Practice Regularly:
Conduct drills and simulations quarterly.
Encourage Learning:
Document experiences honestly and use them to improve plans.
Embrace Technology:
Leverage automation, monitoring tools, and analytics to strengthen each stage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best plans, mistakes can undermine resilience:
- Ignoring early warning signs
- Failing to test plans regularly
- Lacking clear communication channels
- Overlooking emotional and human impacts
Avoid these to ensure your resilience framework remains effective.
Future Relevance of Resilience Lifecycle Framework
As the world becomes more interconnected and change accelerates, resilience will be a defining trait of successful organizations and individuals alike. With evolving risks from climate change to digital threats understanding what are the 5 key stages of resilience lifecycle framework is essential for sustained growth and stability.
Conclusion
Resilience is not a one‑time achievement but a continuous cycle of learning and strengthening. By mastering what are the 5 key stages of resilience lifecycle framework Anticipation, Preparation, Response, Recovery, and Adaptation you gain a proactive approach to uncertainty. These stages empower you to face change with confidence, learn from adversity, and emerge stronger each time.
Embrace this framework, and you won’t just survive you’ll thrive.
FAQs
What is the resilience lifecycle framework?
The resilience lifecycle framework is a structured process defining the stages of building and improving resilience over time.
Why is anticipation important in resilience?
Anticipation helps identify risk early, allowing preparation and planning before disruptions occur.
How does recovery differ from response?
Response acts immediately during a crisis, while recovery focuses on restoring normal operations and improving afterward.
Can individuals use the resilience lifecycle framework?
Yes individuals can apply the stages to personal growth, emotional management, and life planning.
How often should resilience plans be updated?
Ideally annually or whenever major changes or new risks emerge.